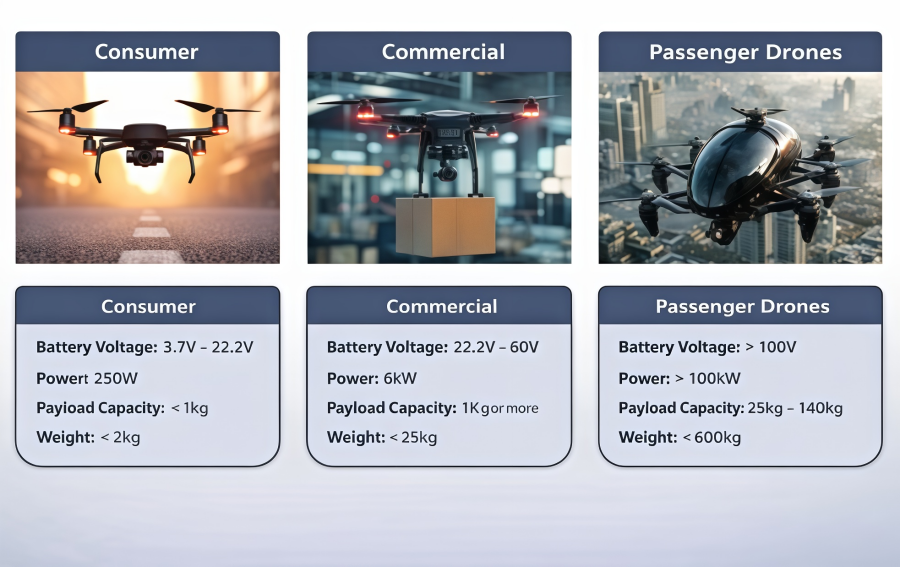
As drone technology continues to mature, these aerial platforms are changing many industries with efficient and flexible solutions. In agriculture, drones support precision farming, crop monitoring, and livestock tracking. In industry, drones are used for site surveys, infrastructure inspection, and project monitoring. In logistics and public services, drones are also transforming delivery methods. To ensure superior data quality and safety, developers are increasingly prioritizing drones with best image sensors.
Among many key technologies, autonomous navigation and perception systems are the foundation of intelligent and safe drone flight. By combining multiple sensing methods, drones can detect their surroundings in real time and perform positioning and path planning. Image sensors play a critical role in environment recognition, object detection, and visual navigation. This article focuses on how these drone systems are implemented and the role of image sensors for it.
Typical Applications of Drones
Drone technology is rapidly expanding across many industries. From mapping and inspection to agriculture and logistics, drones are no longer just aerial cameras but efficient work platforms with intelligent systems. The following sections introduce typical drone applications and their use in different industries.
1. Mapping Drones
Mapping drones are typically equipped with high-resolution cameras and depth-sensing sensors. They are used to collect accurate geographic data and generate high-precision maps and 3D models. Common applications include construction planning, mining surveys, and environmental monitoring.
2. Inspection Drones
Inspection drones integrate thermal imaging devices and various sensors to examine infrastructure such as bridges, power lines, and pipelines. They can collect real-time data and quickly detect potential issues like cracks and corrosion.
3. Agricultural Drones
Agricultural drones use multispectral sensors to monitor crop growth conditions. They support irrigation management, pest and disease detection, and precise spraying of pesticides and fertilizers, driving the development of modern precision agriculture.
4. Delivery Drones
Delivery drones are designed primarily for cargo transport. They are used in logistics, healthcare, and e-commerce, enabling fast material delivery while improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
5. Surveillance and Security Drones
These drones are equipped with high-definition cameras and thermal imaging systems. They can monitor large areas continuously and detect abnormal activities or intrusions, enhancing overall security.
6. Heavy-Lift Drones
Heavy-lift drones feature strong payload capacity. They are suitable for transporting materials and equipment in construction, disaster response, and logistics applications, meeting demanding operational needs.
7. Environmental Monitoring Drones
Environmental monitoring drones are used to collect data on air quality, water conditions, and wildlife activity. They provide reliable data for ecological research, environmental protection, and resource management.
8. Emergency Response Drones
In disaster and emergency situations, emergency response drones can deliver medical supplies, search for survivors, and assess damage. Combined with thermal imaging and loudspeaker systems, they help improve rescue efficiency.
9. Construction Drones
Construction drones are widely used for site surveys, construction progress tracking, and safety inspections. By providing real-time data and high-resolution imagery, they enable more efficient project management and decision-making.
UAV Autonomous Navigation System
Image and depth sensors are key electronic parts of a drone's navigation system. They provide the important data needed for the drone to sense its environment. Image sensors help drones navigate by recognizing and tracking visual markers, which is very useful in places where GPS is not available. With these sensors, drones can detect obstacles, follow planned routes, and adjust their flight based on real-time visual data.
The visual data from image sensors is processed by advanced computer vision algorithms. That allows drones to understand complex scenes and make smart decisions. At the same time, depth sensors send out laser pulses and measure the reflection time, and create a precise 3D map of the surrounding environment.
By combining image and depth data through sensor fusion, drones can safely fly through complex terrain even in low light or visually challenging conditions. The combination of visual and depth sensing improves the drone's situational awareness. It enables obstacle avoidance, precise navigation, and autonomous decision-making, which are crucial for reliable operation in diverse environments.
GPS navigation is another important technology for drones. It works by receiving signals from satellites and calculating the drone's exact position. GPS guides the drone to follow set waypoints. However, in places like indoors, dense forests, or urban canyons with tall buildings, GPS signals can be weak or lost. By combining GPS with image and depth sensors, drones can switch smoothly between different navigation methods and maintain accurate positioning even when GPS signals are weak or unavailable.

Drone Perception System
When choosing image sensors for a drone, it is essential to consider the specific application and requirements. A drone system typically uses six to eight sensors, but in some cases, up to twelve sensors may be deployed.
Global shutter sensors capture the entire frame at once, making them ideal for imaging moving objects. They effectively prevent image distortion and motion artifacts, which is crucial for high-precision tasks such as mapping, surveying, and industrial inspection. By capturing the full frame in a single shot, global shutters eliminate common issues like the “jello effect” and motion blur seen in rolling shutter sensors.
l Low-power image sensors: Consume less energy, making it easier to deploy multiple sensors for a comprehensive view of the scene.
l High Dynamic Range (HDR) cameras: Capture clear, detailed images under varying lighting conditions.
l High resolution: Higher pixel counts enhance the drone’s capability, enabling more precise and detailed inspections and surveys.
l Extended vision: SWIR (Short-Wave Infrared) sensors allow observation beyond the visible light range.
Ande Electronics: Your Partner for Intelligent Drone Upgrades
As a trusted partner for intelligent drone upgrades, Ande Electronics offers a wide range of electronic components, including high-quality image sensors. These sensors are not only widely used in drone perception systems but also find applications in autonomous driving, security surveillance, industrial automation, smart robotics, and smart city projects. With advanced technology and strict quality control, Ande Electronics’ sensors meet the demands of diverse applications for accuracy, reliability, and high performance, providing dependable electronic solutions across industries.
Start your journey with Ande today and leverage our selection to build drones with best image sensors that deliver clear and precise visual data, enabling efficient, safe, and intelligent application upgrades.